LR Circuit with DC Source
LR Circuit with DC Source: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Derivation of Decay of Current in L-R DC Circuit, Half-Life in L-R DC Circuit, L-R DC Circuit, Time Constant in L-R DC Circuit, DC Circuit, Derivation of Growth of Current in L-R DC Circuit, etc.
Important Questions on LR Circuit with DC Source
In the circuit shown, the power consumed by the bulb long after the key is closed is (inductor is ideal)
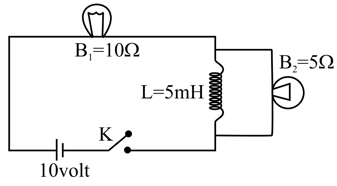
In the given circuit key is closed at . At what time the potential difference across inductor is one fourth of emf of the cell.
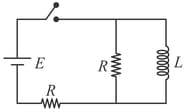
Time constant of the given circuit is
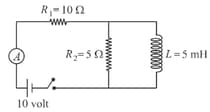
In the circuit shown the reading of ammeter long time after the key is closed is
In a particular R-L series circuit a voltage of at produces a current of while the same voltage at produces . What are the values of and in the circuit ?
In the circuit current through source will be [Given ]
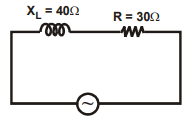
In the circuit shown in the figure, . Switch is closed at time . The current through and would be equal after a time equal to
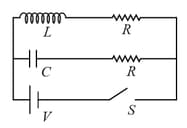
In the given circuit, the battery has emf and negligible internal resistance, the inductance of the inductor . Find the potential drop across the inductor as a function of time, if at switch is closed.
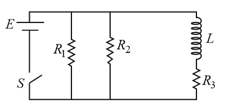
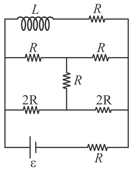
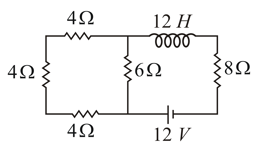
The time constant of the given circuit, containing an inductor and few resistors, is
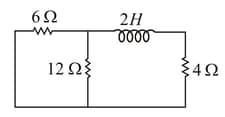
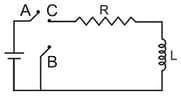
In the circuit shown here, the point '' is kept connected to point '' till the current flowing through the circuit becomes constant. Afterwards, suddenly, point '' is disconnected from point '' and connected to point '' at time . Ratio of the voltage across resistance and the inductor at will be equal to:
When a circuit with is connected in series to an source of voltage a maximum rms current of is observed at frequency If this circuit is now connected to a battery of emf and internal resistance of the current will be
Consider a part of network as shown below:
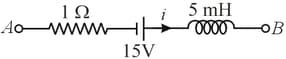
If at a certain instant, the current is and it is decreasing at the rate of , then is,
In the inductive circuit given in the figure, the current rises after the switch is put on. At instant when the current is then potential difference across the inductor will be :-
, respectively, indicate inductance, capacitance and resistance. Select the combination which does not have dimensions of frequency.
Identify the correct statement out of the following options regarding the given circuit.
For a certain inductive coil, it is known that its time constant is . If a resistance is joined in series with the coil, the time constant becomes . Hence, find the inductance and resistance of the coil.
With respect to the given L-R circuit, is the initial current and is the steady state current through the battery. Then, calculate the ratio .
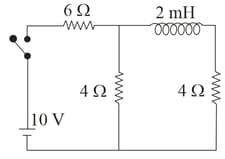
In a circuit, an inductance of and a resistance of are connected in series to a source of voltage . What is the time when the current in the circuit reaches half of its steady state value?
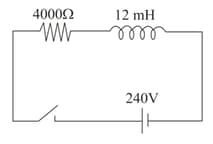
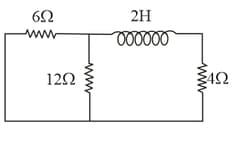
Calculate the time constant for the adjoining circuit that contains an inductor with a few resistors.
How much time does a solenoid of resistance require, to attain the magnetic energy equal to of its maximum magnetic energy, when connected to a battery?
